Radioembolization
(46) Holmium-166 Microspheres for Theranostic Transarterial Radioembolization of HCC: Particle traits & Dosimetry
Saturday, October 18, 2025
6:00 PM - 7:30 PM East Coast USA Time
Saad Badat, BA – Medical Student, Northeast Ohio Medical University; Mina Makary, MD – Clinical Assistant Professor, Division of Vascular and Interventional Radiology, The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center
Purpose: The purpose of this educational exhibit is to review the unique physical and imaging properties of Holmium‑166 (Ho‑166) microspheres, and examine their clinical advantages and ongoing research in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) using transarterial radioembolization (TARE).
Material and Methods: We conducted a literature review of key differences between Ho‑166 and traditional Y‑90 microspheres including emission characteristics, imaging capabilities, and dosimetry. We assessed prospective, retrospective, and early-phase clinical trial data.
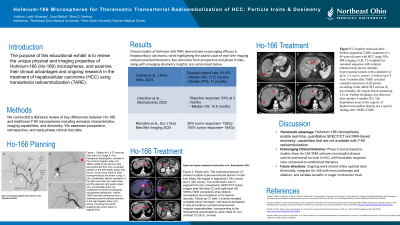
Results: Clinical studies support the safety and efficacy of Ho‑166 TARE in HCC treatment. In a phase II trial, patients demonstrated a disease control rate of 81.8%, with a median overall survival (OS) of 17.2 months and progression-free survival of 11 months. Additionally, Grade 3-5 toxicities were limited ( < 10%), and treatment‑related unacceptable toxicity occurred in only 3 of 31 patients. Another prospective study reported a 54% objective response rate at 3 months and a median OS of 14.9 months, with minimal toxicity. Tumor-absorbed doses ≥155 Gy were significantly associated with better outcomes. Ho‑166's gamma emission enables real-time SPECT/CT imaging and MRI-based dosimetry, offering precise post-treatment assessment of microsphere distribution.
Conclusions: Holmium‑166 TARE introduces a novel theranostic platform with real-time imaging and precision dosimetry. Future directions include integrating Ho‑166 into personalized treatment planning, refining tumor-specific dose thresholds, and exploring combination strategies with ablative and immunotherapeutic modalities to enhance clinical outcomes in HCC.
Material and Methods: We conducted a literature review of key differences between Ho‑166 and traditional Y‑90 microspheres including emission characteristics, imaging capabilities, and dosimetry. We assessed prospective, retrospective, and early-phase clinical trial data.
Results: Clinical studies support the safety and efficacy of Ho‑166 TARE in HCC treatment. In a phase II trial, patients demonstrated a disease control rate of 81.8%, with a median overall survival (OS) of 17.2 months and progression-free survival of 11 months. Additionally, Grade 3-5 toxicities were limited ( < 10%), and treatment‑related unacceptable toxicity occurred in only 3 of 31 patients. Another prospective study reported a 54% objective response rate at 3 months and a median OS of 14.9 months, with minimal toxicity. Tumor-absorbed doses ≥155 Gy were significantly associated with better outcomes. Ho‑166's gamma emission enables real-time SPECT/CT imaging and MRI-based dosimetry, offering precise post-treatment assessment of microsphere distribution.
Conclusions: Holmium‑166 TARE introduces a novel theranostic platform with real-time imaging and precision dosimetry. Future directions include integrating Ho‑166 into personalized treatment planning, refining tumor-specific dose thresholds, and exploring combination strategies with ablative and immunotherapeutic modalities to enhance clinical outcomes in HCC.
