Radioembolization
(15) Voxel-Based Dosimetry in Y90 Radioembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Paradigm Shift in Treatment Planning
Saturday, October 18, 2025
6:00 PM - 7:30 PM East Coast USA Time
Marcus Hong, BA – Medical Student, Ohio State University; Mina Makary, MD – Principle Investigator, Ohio State University
Purpose: To evaluate how voxel-based dosimetry influences treatment planning, therapeutic efficacy, and clinical outcomes in Yttrium-90 (Y90) radioembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), compared to traditional dosimetric approaches.
Material and Methods: A targeted literature review was conducted to assess the clinical utility of voxel-based dosimetry in Y90 radioembolization for HCC. Sources included clinical studies, retrospective analyses, and dosimetric modeling reports focused on personalized treatment planning. Primary outcomes included tumor-absorbed dose, treatment efficacy, and comparisons to conventional methods such as body surface area and partition models. Emphasis was placed on the role of voxel-based techniques in optimizing outcomes through patient-specific dosing.
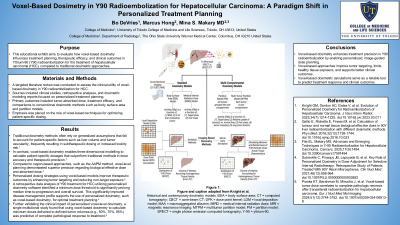
Results: Traditional dosimetry methods rely on generalized assumptions that may overlook patient-specific factors such as liver volume and tumor vascularity, often leading to subtherapeutic dosing or increased toxicity risk. In contrast, voxel-based dosimetry provides three-dimensional, patient-specific dose calculations that enhance accuracy and precision. Compared to standard and region-based methods, voxel-level planning shows stronger correlation with treatment response and outcomes. Personalized dosing strategies using voxel-based models improve therapeutic results by enhancing tumor targeting and limiting non-target exposure. Retrospective data show that reaching threshold tumor doses using voxel-based planning significantly increased median time-to-progression and overall survival. Additional studies found that minimum doses delivered to 50%, 70%, and 95% of tumor volume were predictive of complete pathological response, reinforcing the clinical value of voxel-level dosimetry.
Conclusions: Voxel-based dosimetry enhances treatment precision in Y90 radioembolization by enabling personalized, image-guided dose planning. This approach improves tumor targeting, limits healthy tissue exposure, and supports better clinical outcomes, positioning it as an essential tool in modern HCC management.
Material and Methods: A targeted literature review was conducted to assess the clinical utility of voxel-based dosimetry in Y90 radioembolization for HCC. Sources included clinical studies, retrospective analyses, and dosimetric modeling reports focused on personalized treatment planning. Primary outcomes included tumor-absorbed dose, treatment efficacy, and comparisons to conventional methods such as body surface area and partition models. Emphasis was placed on the role of voxel-based techniques in optimizing outcomes through patient-specific dosing.
Results: Traditional dosimetry methods rely on generalized assumptions that may overlook patient-specific factors such as liver volume and tumor vascularity, often leading to subtherapeutic dosing or increased toxicity risk. In contrast, voxel-based dosimetry provides three-dimensional, patient-specific dose calculations that enhance accuracy and precision. Compared to standard and region-based methods, voxel-level planning shows stronger correlation with treatment response and outcomes. Personalized dosing strategies using voxel-based models improve therapeutic results by enhancing tumor targeting and limiting non-target exposure. Retrospective data show that reaching threshold tumor doses using voxel-based planning significantly increased median time-to-progression and overall survival. Additional studies found that minimum doses delivered to 50%, 70%, and 95% of tumor volume were predictive of complete pathological response, reinforcing the clinical value of voxel-level dosimetry.
Conclusions: Voxel-based dosimetry enhances treatment precision in Y90 radioembolization by enabling personalized, image-guided dose planning. This approach improves tumor targeting, limits healthy tissue exposure, and supports better clinical outcomes, positioning it as an essential tool in modern HCC management.
